
Pros and Cons Native vs Non-Native Mobile App Development Tools
There are two primary categories of mobile app development tools: native and non-native. Each offers distinct advantages and disadvantages. The optimal choice for your organization will depend entirely on your specific project requirements and budget.
To help you decide which mobile app development path aligns best with your project's goals, let's explore the key differences between native and non-native mobile app development tools:
Native App Development : Mobile Apps develop specifically for one platform (iOS or Android) using platform-specific languages and tools.
Popular Tools & Languages :
- iOS: Swift, Objective-C, Xcode
- Android: Kotlin, Java, Android Studio
Pros :
- Best performance and responsiveness
- Superior UI/UX tailored to platform guidelines
- Full access to device features (camera, GPS, sensors)
Cons :
- Higher development cost (Software code not reusable in other platform)
- Requires specialized developers proficient in platform-specific languages and environments.
- Involves longer development cycles due to platform-specific coding and potential for maintaining separate codebases.
Definition : Apps built to run across multiple platforms such as IOS, Android or Huawei App Gallery using a single codebase.
Subcategories & Tools :
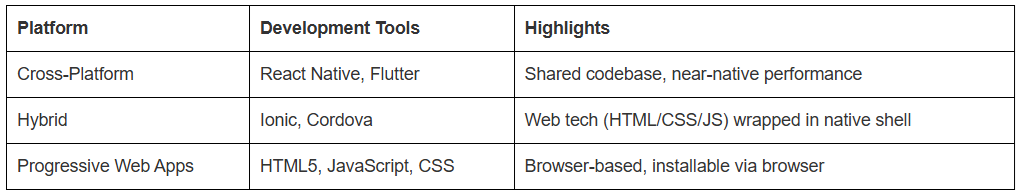
Pros :
- Cost-effective since software coding support all platforms (one team, one codebase).
- Accelerated Development Cycles : Benefits from a single codebase, streamlining the development process.
- Broader Cross-Platform Reach : Allows the application to be deployed across multiple operating systems from a single development effort.
Cons :
- Potential Performance Limitations : Since the application isn't exclusively optimized for a single platform, it may experience performance constraints.
- Non-Native UI Feel : User interfaces might not perfectly align with platform-specific design guidelines, resulting in a less integrated native look and feel.
- Restricted Access to Device Features : Compatibility limitations with development tools can hinder full access to advanced or newly released device functionalities.

